Direct Speech
Direct speech repeats or quotes the exact words that the person said. when people use direct speech in written form, They put the spoken words between marks (""), and these words are unchanged. it is like a telephone conversation.
Some examples are:
As you can see in the example, there is a part called indirect speech. This is the opposite of direct speech.
Indirect Speech
Indirect speech is usually used to talk about the past. So, people usually change the tense of the words spoken. In indirect speech, people use words such as "Tell", "Say", "Ask", and the word "that" to emphasis what the person said, and in the written way, people do not use commas.
It is important to take into account that each verb tense has a specific time when what someone said is reported.
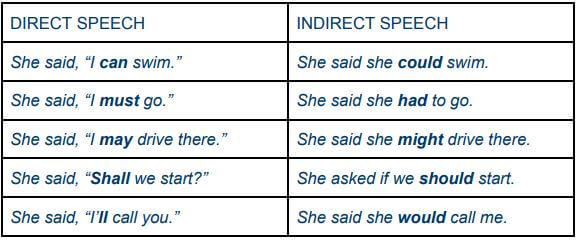
In that image, you can see each tense in direct speech, and how they change in indirect speech
Video